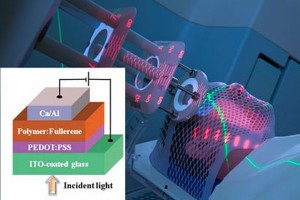
Usually when the word distribute and it’s derivatives are used in relation to solar, it’s in terms of distributed generation. But the Clean Energy Project led by a team of researchers at Harvard University, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico and Haverford College are using distributed computing to identify the most likely molecules to foment the next generation of organic photovoltaics, and fuel cells and they need your—well your computer’s—help!
The distributed computing model has been used to search the stars for aliens, to research new drugs for cancer and Parkinson’s and other uses. Now it’s being put to use to help develop organic photovoltaic molecules to produce alternatives to photovoltaics that use inorganic compounds or hazardous materials.

 Follow
Follow