Skinny playerSkinny music player concept is powered by body heat
As we know it:
The recent advancement in portable electronics has given humankind a variety of gadgets to keep oneself entertained and connected with the rest of the world. However, this advancement comes at the cost of energy, which as we all know isn’t clean in all cases. The advancements in nanotechnology and material science are causing energy requirements to fall, but at the same time since the production of these gadgets is increasing, the global energy demand for these devices is getting out of bounds.
Need for change:
Researchers over the globe are working on next-gen devices that run on renewable sources of energy, such as solar energy, wind energy and some other unconventional forms of energy such as human body heat. A team of German scientists have identified mechanism of converting body heat into usable electricity. This could revolutionize the portable electronics industry, as most portable electronic gadgets are handheld and can ideally be charged with body heat. However, it is impossible to capture 100 percent body energy under any circumstances. This is why body heat can only be converted in three per cent efficiency with current thermoelectric materials.
What’s next?
1. Texas Instruments to manufacture chips powered by body heat
Chip powered by body heatChip designed by Texas Instruments
What’s new?
Texas Instruments have come up with a tremendous innovation that allows your mobile phone batteries to get charged just through the warmth of your body. The researchers at Texas Instruments say that this energy efficient future chip will consume a tenth of what the present chips are using.
What difference will it make?
Joyce Kwong, a graduate at MIT(Michigan Institute of Technology) along with Professor Anantha Chandrakasan quoted that earlier chips worked at 1V but with the creation of future chips , they would be able to operate with merely 0.3 volts as well. This is a great improvement over the previous times indeed where 1-2 volts were required. This new invention was made possible with the reduction in voltage pumping around the chips.
Problems
Professor Chandrakasan however also quoted that making future chips run at 0.3 volts requires major work as the memory and logic circuits would have to be designed in such a way that they could run at such low voltages. Therefore they tried to construct a DC-To–DC converter which works by reducing the voltage to a lower level on the chip.
The purpose is to use the body heat and enable the technology which would be useful for body are networks and wireless body sensor networks like the informational exchanges between mobiles and music players. The difficulty in this innovation lied in the variations encountered in chip manufacturing which was the major barrier to further development .
2. Skinny music player concept is powered by body heat
Skinny playerSkinny music player concept is powered by body heat
What’s new?
Designers have already started conceptualizing portable music players that can be powered by body heat. This Skinny Music Player concept is put forth by Chih-Wei Wang and Shou-His Fu. The user need not connect any headphones and could simply listen to the music through the power control.
What difference will it make?
Since the device has been designed in a way that it extracts body heat to generate power with a flexible battery charging device which comes in to bodily contact whenever it is used. This also eliminates the need for thought of charging batteries before you set out for your daily exercise.
3. Dyson energy bracelet a good call
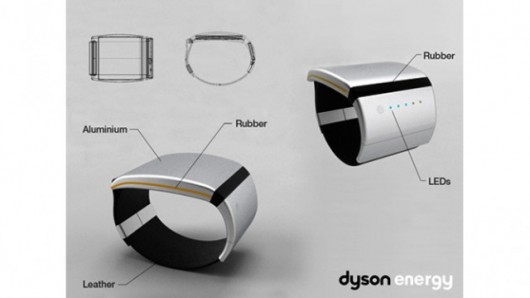
Dyson energy braceletDyson energy bracelet design using body heat and ambient temperature to produce electricity
What’s new?
Dyson’s Energy Bracelet is based on a technology that converts the temperature difference between the user’s skin and the ambient air outside and stores it in a battery. This phenomenon is called as Seebeck effect. This energy bracelet generates enough electricity to jolt your cell phone’s dead battery and allows to make that one important call.
What difference will it make?
The designers of this bracelet had tested a peltier element by creating heat and cold on the same component and found that through the Seebeck Effect that electricity was being produced. Designers however tell that to have a dozen minutes of conversation, a few hours are required to power the cell phone. But unfortunately when the mobile phones need a sudden charging then it is to be plugged in to a functional bracelet which looks mockingly similar to those detention home devices worn around the ankles.
Problems
The major problem is that this bracelet does not provide a full recharge and allows only some extra minutes of talk time on your cell phone.
4. MEMS device generates power from body heat
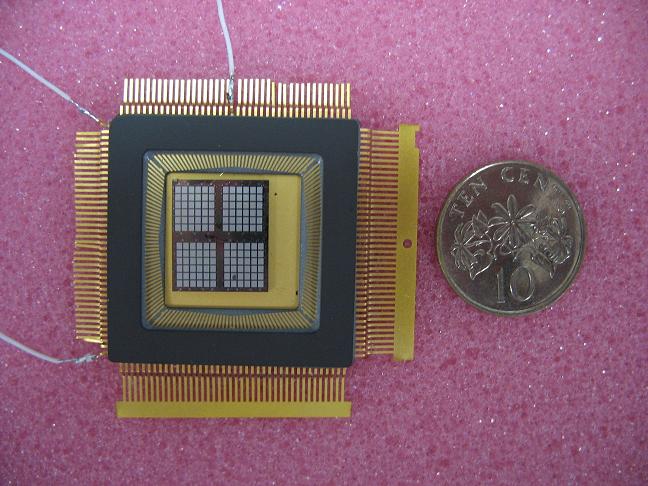
Thermo Electric Power GeneratorMEMS device generates power from body heat
What’s new?
A team of researchers from Singapore have designed an energy producing device that generates electricity from the body heat or the surrounding environment where there is a temperature difference. This device is when attached to the body is able to generate a few micro-watts of power, which can be used for medical devices and sensors, mostly wireless.
What difference will it make?
Though such body heat using devices have previously been invented as well but this new thermoelectric power generator has been combined with a lot of new features. These new features include:a heart-sink layer, a peripheral cavity and vacuum cavities which are powered at increasing the temperature difference. This variation in temperature is increased between the parts exposed in the ambient air and the part of the generator that uses the body heat as larger the variation in temperature, greater is the output of the voltage.
Problems:
The main problem with this device is that it only delivers a few microwatts of electricity which can only be used for wireless sensors and embedded medical devices.
5. The human battery: Turning body heat into electric power
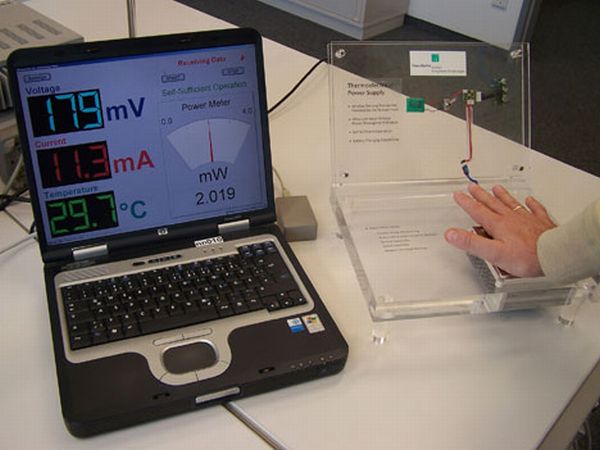

Body heat powerTurning body heat into electric power
What’s new?
The Fraunhofer Institute is currently deployed in developing Power Sponges; that basically uses body heat to power almost anything strapped to their body. This could include medical devices and cell phones etc. Power sponges work through TEG technology i.e. thermoelectric generators which produce electricity through temperature difference. Earlier to this invention, the generators used to require difference of several tens of degrees to produce electricity. But now with the introduction of new circuitry , it has been made simpler and now it could run merely on 200 millivolts.
What difference will it make?
The difference that this device has brought is that it does not require an internal battery to charge to enable running of devices but takes energy solely from body heat. Circuits that operate at 50 milivolts already exist and Peter Skies, the project manager at Fraunhofer Institute says that they are aiming for improvements with the introduction of switching systems which would allow a small difference of 0.5 volts to generate electricity.
Problems
The problem as quoted by Peter Skies is that ‘there would only be a fewer degrees of difference between the environment and the body’s outer temperature and this only low voltages could be produced from such low temperature differences.
 Follow
Follow