Wireless charging is charging batteries without cables or device-specific AC adaptors.
As we know it
Petrol burning personal cars, about 50 million of them produced per year, account for some 20% of the 8000 million tons of CO2 that we infuse into the atmosphere annually. The world is therefore looking at electric cars as an important step towards limiting this emission. Every major car maker around the world is introducing new electric vehicles each year and concerned people are beginning to buy EVs despite the high price tag.

One of the principal concern for an EV user is the battery capacity. A typical petrol engine car has a tank capacity that gives some 500 km of driving range before it requires re-fueling. Current EVs have a battery capacity that can at best give some 120-150 km before it needs a recharge . Such a battery already weighs around 150 kg, so fitting a larger battery is not a solution. Therefore, it must await the availability of improved batteries with far better power to weight ratios than is currently possible.
In addition, battery recharging is a slow process that typically could take a minimum of 2 hours and even up to 12 hours. This is in sharp contrast to petrol refilling that takes just few minutes. The gas stations for refueling, in over 100 years of petrol usage are never more than few kilometers from any road whereas EV recharge stations are still being installed. These issues have led to the users buying a hybrid vehicle that incorporates a petrol engine into an EV.
Even when the EV is used in a city environment, where recharge stations will eventually be plentiful, plugging in a charging cord is still not the best solution. Though, many of the early concerns with safety from electric shock have been overcome by the improved designs of the current outlets and the charging cord, many drivers still find the process unfamiliar and difficult. In addition , there have been issues with people forgetting to unplug before driving the car away and so on.
The need for change
There would be much easier acceptance of EVs if there was an easier way to recharge batteries than the present method of plugging in a cord into a power outlet. Also if the re-charging can be accomplished without the need of any special effort by the driver.
What’s next
The concept of wireless recharging of the EV battery is gaining traction with many of the leading car manufacturers teaming with technology companies to test pilot models. The technology is not new and it has been used with electric toothbrushes for over 10 years and there are devices to recharge mobile phones using inductive chargers. The challenge is to apply it to the much greater power needed for an EV.
1. Toyota Teams Up With WiTricity for Wireless Car Charging
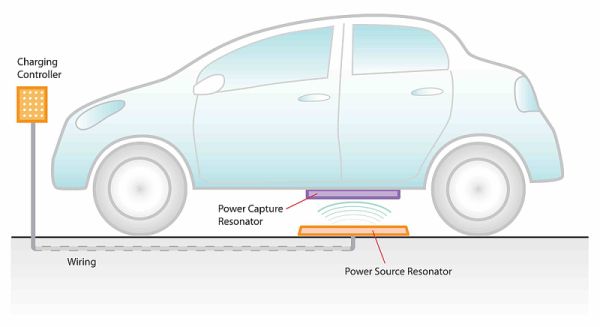
Toyota and WiTricityThis technology uses resonance ferrying electricity through a magnetic field.
Toyota has teamed up with WiTricity of Massachussets, a start-up working with MIT technology, to launch the Power Source Resonator. In this, a pad, the size of a pizza box, containing a high frequency coil and power electronics components is embedded in the floor of a car garage or in a parking lot. The underside of the car is fitted with a matching power capture plate . The power source resonator is connected to the utility 240 volt power source and produces a high frequency ( 20kHz or higher ) electromagnetic field. This field induces an electric current in the coil contained in the power capture plate fitted to the car and that alternating current is rectified to DC and charges the battery.
WiTricity affirms that its unit can deliver 3.3KW of power at about 90% efficiency ( i.e to deliver 3.3kW it will take in some 3.7kW of power). The concept is certainly very attractive, the driver of the EV just parks the car in the garage or a parking lot and activates the recharge process while he/she is at home or at work or even, shopping .
The problem
The Toyota EV is expected to have a battery of 22 kWh which means that a near – drained battery would take over 6 hours to charge. The assumptions Toyota and WiTricity make is perhaps that the battery would usually need only “top-up” charging and that could be easily accomplished in the 30 to 60 minutes while the car would be in a shopping mall lot . Cars parked at home or at work would have more time and accomplish full recharge.
2. Volvo focuses on wireless charging to electric cars
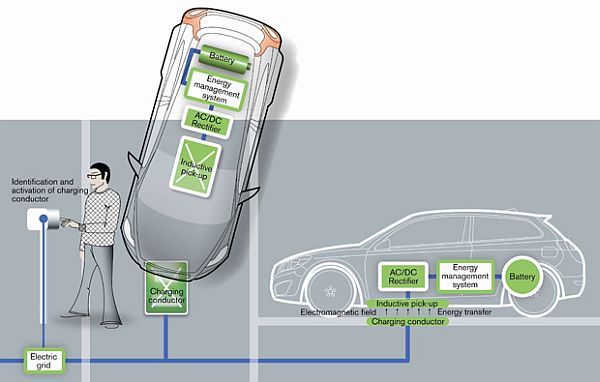
VolvoThis technology charges vehicle through charging plates which contain coils that generate magnetic field.
Volvo in partnership with a Belgian technology company has suggested inductive charging not just when the car is parked, but when it is being driven. They suggest that select lanes of a highway, designated for EVs, could be embedded with a charging conductor that continually generate inductive fields that the receptor in the car picks up to recharge its battery.
While this could overcome the issue of long recharge time for the batteries, it appears unlikely to be economical until the population of EVs begin to be more significant than they are now. Even in London, which aims to be the EV capital of Europe, the total number of electric and hybrid cars in use is only some 17000 compared with the total car population of over 3 million.
3. HaloIPT launches world’s first market-ready wireless charging system for EVs
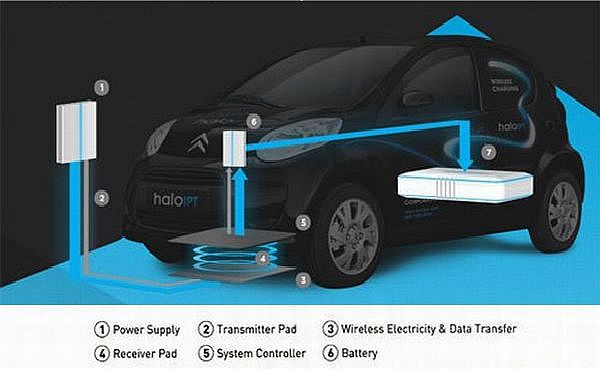
HaloIPTThis technology charges vehicle automatically when parked or driven on roads.
HaloIPT, a New Zealand based technology company, in partnership with Arup the engineering company, has debuted its own version of the Inductive Wireless charging station. The London city council already offers a number of incentives to the use of EVs in the inner city area including the free recharging for an annual membership fee from power outlets being set up all around .This new technology could help accelerate the process of adoption of EVs.
HaloIPT has also suggested electrification of Motorways to provide continuous re-charging that could improve acceptance of EVs for passenger commuting needs.
4. Evatran unveils wireless charging solution for electric vehicles.

Evatran wireless chargingIts Plug less Power induction charging solution for electric vehicles.
Evatran of Virginia, a spinoff from a transformer manufacturer, has demonstrated its inductive charging station named “Plugless Power”. One major fillip for this company is that Google Inc. has installed one of Evatran’s recharge stations at it Mountainview office building as a measure to encourage employees to consider shifting to EVs. Google’s example of corporate citizenship could trigger adoption by other corporates which could help persuade employees to change to EVs.
The problem
Though inductive wireless charging appears to be the coming technology, the car makers, so far, have not got on-board which requires the EV user to retrofit this device, at around $ 5000. That could change soon as Nissan has announced that its new EV models will have inductive charging as a built-in feature. The Society of Automotive Engineers ( SAE ) also appears to have determined this to be the coming technology in forming a task force to write the first industry standard for inductive charging of EV batteries.
In summary
With several major car companies endorsing the inductive charging technology, we should expect this to become the industry standard and with user education and wider deployment. Wireless recharging of batteries in electric cars should find wide acceptance.

 Follow
Follow