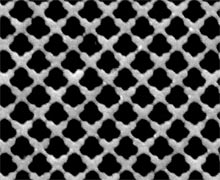
A new nanostructured material that absorbs a broad spectrum of light from any angle could lead to the most efficient thin-film solar cells ever.
Researchers are applying the design to semiconductor materials to make solar cells that they hope will save money on materials costs while still offering high power-conversion efficiency. Initial tests with silicon suggest that this kind of patterning can lead to a fivefold enhancement in absorbance.
Conventional solar cells are typically a hundred micrometers or more thick. Researchers are working on ways to make thinner solar cells, on the order of hundreds of nanometers thick rather than micrometers, with the same performance, to lower manufacturing costs. However, a thinner solar cell normally absorbs less light, meaning it cannot generate as much electricity.
 Follow
Follow